Are you curious about the ins and outs of straight time pay?
Whether you're stepping into the workforce, running a business, or just brushing up on your payroll knowledge, understanding straight time pay is fundamental.
It's the backbone of most paychecks, and getting a grip on it can clear up a lot of paycheck mysteries.
Let's see how it works in the real world.
What is straight time pay?
Imagine you have a job where you're paid by the hour. Straight-time pay is the money you earn during your regular working hours, not including overtime or bonuses.
Let's say you work 40 hours a week. If your hourly rate is $15, your straight-time pay is simply 40 hours multiplied by $15. That's your pay for a standard workweek, without any extra hours or special bonuses. It's the basic pay you can count on for the time you've worked.
In short, straight-time pay is just your regular pay rate times the number of hours you work. Plain and simple.
Straight time pay and overtime pay and hourly pay - differences
They're all about how you get paid for the time you work, but they have their own little quirks.
Let's put them in a table to make it clear:
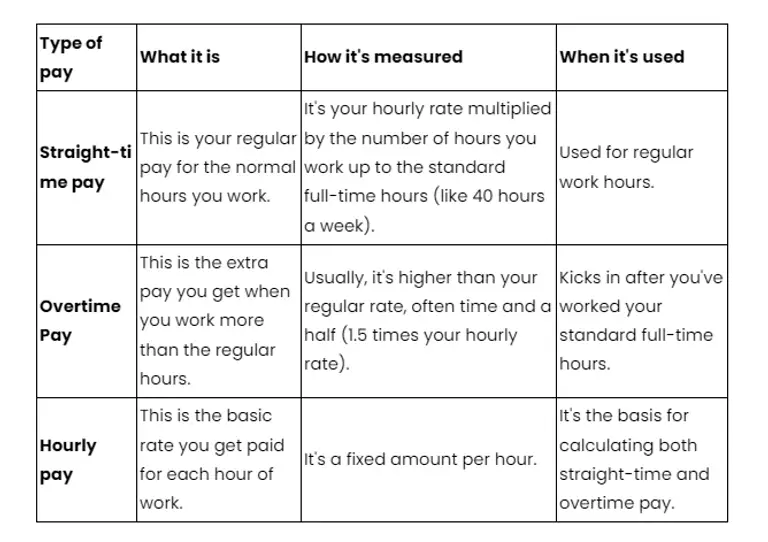
So, in simple terms:
- Straight-time pay is your standard paycheck for a regular workweek.
- Overtime pay is the bonus cash for those extra hours beyond your normal schedule.
- Hourly pay is the basic building block, the rate you get for each hour you work, no matter what.
Each type of pay has its place depending on how much and when you work. Straight-time for the usual hours, overtime for the extra effort, and hourly is the rate that decides it all.
Guide to calculating straight-time Pay for HR professionals

As an HR professional, you must know how to accurately count straight-time pay. All while ensuring compliance with the Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA) and fair compensation for employees.
Here's how to do it:
Determine the regular rate of pay
Establish each employee's hourly net and gross wage. This rate is the agreed-upon payment for each hour they work. Make sure it meets or exceeds the FLSA's minimum wage requirements.
Record hours worked
Accurately track the total hours worked by each employee during the pay period. This includes all standard work hours but excludes overtime hours. A typical full-time schedule is 40 hours per week.
Calculate straight-time pay
Multiply the employee's hourly wage by the total number of hours worked. For example, if an employee's hourly wage is $20 and they have worked 40 hours in a week, an hourly to salary calculator tells you that their straight-time pay would be 20 dollars times 40 hours, equaling $800 per week.
FLSA compliance
The FLSA mandates that non-exempt employees receive overtime compensation at a rate of time and a half for each hour of overtime worked beyond the standard 40-hour workweek. Check whether your payroll system differentiates between straight-time and overtime pay.
Manage exempt employees
Exempt employees are generally not eligible for overtime pay. Their compensation is often based on a salaried basis, rather than an hourly one. What's more, it doesn't typically change based on the exact number of hours worked.
Incorporate paid time off (PTO)
For calculating straight-time pay, include PTO such as vacation or holiday hours in the total hours worked, as per your organization's policy.
Hour of overtime consideration
While calculating straight-time pay, be mindful of not including any overtime. Overtime hours are compensated differently, typically at a 1.5 rate.
Total amount of money an employee earns
The straight-time pay calculation is crucial in determining the total amount of money an employee earns during a standard pay period, excluding any overtime compensation.
When you follow these steps, you'll ensure a thorough and compliant approach to calculating straight-time pay for your employees.
Straight time pay legislation in different areas
Straight-time pay legislation, which generally involves the calculation of regular hourly wages for standard work hours, can vary slightly from state to state in the USA.
Most states adhere to the guidelines set by the Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA), but there can be local variations.
Here's a brief comparison:
General FLSA Guidelines
The FLSA, a federal law, establishes the framework for straight-time pay, including provisions for minimum wage and overtime pay.
It typically requires that employees be paid at least the federal minimum wage for up to 40 hours per week, and time and a half for any hours spent working over 40 in a workweek.
Take a look at how it works in different states:
Kansas
Kansas has a unique provision where the standard for overtime pay starts after 46 hours, as opposed to the 40-hour rule.
Minnesota
In Minnesota, the threshold for overtime is set at 48 hours, which is different from the standard rule.
Missouri
In Missouri, state and federal law doesn't allow employees to voluntarily waive their rights to overtime pay and accept straight time instead. Any employer asking an employee to do so violates the law.
Wisconsin and Illinois
These states follow the guidelines closely. For example, Wisconsin calculates straight-time pay by dividing the total wages earned in a week by the total hours worked. Illinois, as of 2023, has set its minimum wage at $13.00 per hour for individuals 18 years and older.
HR professionals and employers need to be aware of both federal and state-specific regulations regarding straight-time pay. This is to ensure compliance and fair compensation for employees. The variations, though minor in some cases, can have significant implications for payroll calculations and labor practices.
How to calculate and track straight time with Unrubble
Managing and tracking straight time with Unrubble is a breeze. It's a great tool for managing not just straight time but also overtime payments and keeping an eye on the annual salary of your employees.
Here's how you can use Unrubble for these tasks:
- Automatic time tracking: Unrubble offers an automatic time tracking feature. This means that as soon as your employees start their workday, Unrubble begins tracking their time. This is perfect for keeping tabs on those standard 8 hours of work.
- Overtime identification: the system is smart enough to detect overtime. So, when an employee works beyond their regular 8-hour shift, Unrubble automatically recognizes this as overtime. This feature is essential for keeping accurate overtime pay.
- Straight time rate calculation: for counting the straight time rate, Unrubble tracks the hours worked up to the standard threshold (like forty hours a week). This data is key for determining the total straight time pay for each employee.
- Annual salary monitoring: if you have employees on an annual salary, Unrubble's tracking features can help you monitor their work hours. This way, you can verify that salaried employees are meeting their work-hour requirements and help them manage their time efficiently.
- User-friendly interface: Unrubble is praised for its user-friendly interface. We know how to make it easy for both managers and employees to use. This simplicity makes time tracking accurate and efficient, without requiring extensive training.
- Real-time reporting: the software provides real-time reporting, which is a great way to keep track of all hours worked, including overtime. This feature helps in making timely and accurate payroll decisions.
- Flexible and adaptable: Unrubble is adaptable to various work environments and can be used on multiple devices. This flexibility is key in today's diverse work settings, where employees might be working from different locations.
In summary, Unrubble simplifies the process of tracking straight time and overtime hours, making payroll more accurate and less time-consuming. Its automatic tracking, user-friendly interface, and real-time reporting capabilities make it an ideal choice for businesses looking to streamline their time tracking processes.
Try it today to see the difference.
Conclusion
And that's the lowdown on straight time pay.
It's a fundamental part of how paychecks are calculated and a key concept in the world of work.
Whether you're clocking in hours as an employee or calculating payrolls in HR, knowing about straight time pay helps keep things clear and fair.
So, the next time you look at a paycheck, you'll know exactly where those numbers are coming from.
And to further boost your efforts, be sure to grab a free trial of Unrubble!
FAQ
What does "straight hours" mean?
"Straight hours" refer to the typical hours an employee works within their regular schedule, compensated at the employee's regular rate of pay, without additional overtime.
What is a straight time shift?
A straight time shift is a work shift where the hours are paid at the employee’s regular rate, and the pay does not include any overtime premiums.
What is the meaning of overtime pay?
Overtime pay is the additional compensation that employees receive for hours worked beyond their normal work schedule, typically calculated at a higher rate than straight time pay.
What is OT Premium?
OT Premium, or overtime premium, is the extra amount paid over the employee's regular pay rate when calculating overtime pay. It is often expressed as "time and a half," which means 1.5 times the regular rate.
How do you calculate straight time pay 1 1?
To calculate straight time pay, multiply the hourly rate by the number of hours worked within the pay period at the employee's regular pay rate. For example, if the hourly rate is $20 and the employee works 40 hours, the straight time pay would be $800.
What is time and a half pay?
Time and a half pay refers to paying an employee 1.5 times their regular rate of pay for overtime hours worked, commonly used to compensate for hours worked beyond the normal schedule.
How to find overtime pay?
To find overtime pay, multiply the number of overtime hours worked by the employee's overtime pay rate, typically time and a half (1.5 times) the employee's regular rate.
What is an hourly rate?
An hourly rate is the amount of pay that an employee earns per hour worked. It is used to calculate both straight time pay and, with additional multipliers, overtime payments for hours worked beyond the standard work schedule.








