Deciding how to structure employee payment schedules can impact cash flow, employee satisfaction, and payroll efficiency. Understanding the differences between semi-monthly vs bi-weekly pay helps businesses select the best system for their needs. Let’s dive into how these schedules work, their benefits, and considerations for choosing the right one.
What is semi-monthly vs bi-weekly pay?

Defining semi-monthly pay
A semi-monthly pay schedule involves paying employees twice a month on fixed dates, often the 1st and 15th or the 15th and 30th. This results in semi-monthly pay periods that are consistent but vary in length, ranging from 14 to 16 days depending on the month. This schedule is common among salaried employees because their wages are typically stable regardless of hours worked.
Defining bi-weekly pay
A bi-weekly pay schedule, on the other hand, pays employees every two weeks, usually on the same day of the week, such as every other Friday. This results in 26 bi-weekly paychecks per year, with some months featuring three pay periods. This schedule works well for hourly employees because it aligns closely with time worked.
Key differences between semi-monthly vs bi-weekly pay
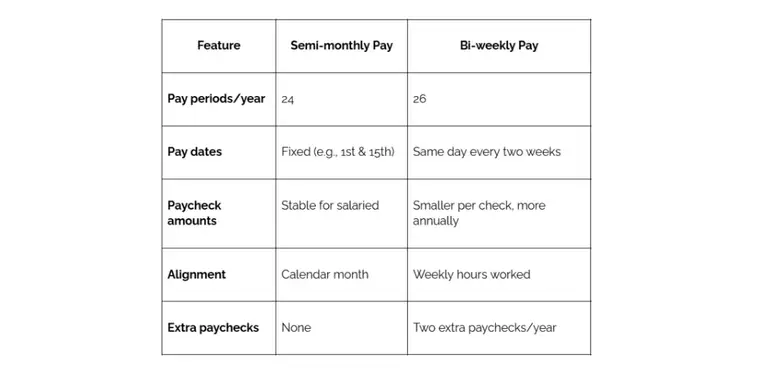
Pros and cons of semi-monthly and bi-weekly pay schedules

Benefits of semi-monthly pay
- Consistent pay dates With a semi-monthly schedule, employees know exactly when they’ll be paid, as pay falls on specific dates like the 15th and 30th. This consistency simplifies managing personal finances for employees.
- Streamlined payroll process For employers, running a semi-monthly payroll means fewer processing events compared to bi-weekly schedules. This can reduce administrative workload, especially for businesses with salaried workers.
- Predictable benefit deductions Calculate benefit deductions more easily with semi-monthly payments, as they align with calendar months. This predictability is helpful for health insurance or retirement contributions.
Drawbacks of semi-monthly pay
- Complex calculations for hourly workers Hourly employees may find semi-monthly schedules confusing, as their hours worked in each pay period can vary. This adds complexity to calculating hourly wages.
- Uneven pay periods Months with varying days can lead to pay periods of different lengths, complicating payroll for new hires or businesses with fluctuating hours making it a good idea to hire an executive assistant to manage these complexities.
Benefits of bi-weekly pay
- Alignment with work schedules For hourly workers, bi-weekly payments align closely with their hours worked, making it easier to calculate overtime and regular pay.
- Additional paychecks Employees paid bi-weekly receive two extra paychecks during the year, creating opportunities for better cash flow management.
- Simplifies tracking hours Employers processing bi-weekly payroll can easily track weekly hours, overtime, and bonuses.
Drawbacks of bi-weekly pay
- More payroll runs Employers must process payroll more frequently, increasing administrative costs and time.
- Smaller paychecks Because there are 26 pay periods, individual paychecks may feel smaller, especially for employees accustomed to monthly budgeting.
Factors to consider when choosing a payroll schedule

1. Employee preferences
Employees’ paychecks are central to job satisfaction. Understanding whether employees prefer predictable semi-monthly payments or frequent bi-weekly payments can guide your decision.
2. Business cash flow
If your business struggles with cash flow, a semi-monthly schedule may provide more stability by requiring fewer payments per year. However, bi-weekly schedules can smooth cash flow for businesses with steady income streams.
3. Payroll frequency
Choosing between weekly and semi-monthly, or bi-weekly and semi-monthly, affects how often employers need to run payroll. Frequent schedules like bi-weekly may suit larger businesses with robust payroll systems, while semi-monthly payroll fits smaller organizations.
4. Hourly vs salaried employees
- Salaried employees benefit from the consistency of a semi-monthly pay schedule, as their wages remain fixed.
- Hourly employees, however, often prefer bi-weekly payroll, as it matches their work patterns and simplifies overtime calculations.
5. Legal and tax considerations
Certain jurisdictions have regulations regarding pay frequency. Ensure your chosen schedule complies with local labor laws to avoid penalties.
Common mistakes to avoid in payroll schedules
1. Overlooking employee types
Mixing hourly workers and salaried workers on the same payroll schedule can create unnecessary complications. Tailor payment systems to employee roles.
2. Mismanaging benefit deductions
Benefit deductions for semi-monthly pay periods may not align perfectly with bi-weekly systems. Ensure accurate tracking to avoid errors in insurance or retirement contributions.
3. Ignoring extra paychecks
Employers using a bi-weekly pay schedule must account for two extra paychecks in their annual budget. Missing this detail can strain finances when three paychecks occur in a month. Learn more about efficient payroll systems with makerspace tools.
How to choose the right payroll schedule

Choosing the most suitable payroll schedule is crucial for maintaining smooth operations, employee satisfaction, and effective cash flow management. The process involves careful consideration of workforce dynamics, financial stability, and communication strategies. Below is an expanded guide on selecting the right payroll schedule, addressing paid semi-monthly, main pay schedules, and other important aspects.
Step 1: Assess your workforce
The first step in determining the right payroll schedule is understanding your workforce composition. Ask these questions to guide your decision:
1. Do you primarily employ hourly employees or salaried employees?
- Hourly employees: A bi-weekly pay schedule works well because it aligns with their weekly hours worked, fitting within the organization's hierarchy and ensuring consistent payroll management across different levels. Employees appreciate knowing their earnings are calculated based on consistent work patterns, especially when overtime is involved.
- Salaried employees: For these workers, paid semi-monthly may be more appropriate as it provides predictable payments on set dates.
2. Do you need flexibility or predictability?
If flexibility is a priority for handling varying hours and shifts, bi-weekly pay can accommodate these changes effectively.
For predictable payday falls, semi-monthly pay periods offer fixed payment dates that salaried employees typically prefer.
Tip: Consider whether the main pay schedules align with your business structure and the preferences of your team. Employees’ satisfaction with how and when they are paid directly affects their morale and productivity.
Step 2: Evaluate cash flow for semi-monthly pay periods
Payroll frequency directly impacts your business’s financial stability and cash flow. The right choice depends on how often your company can comfortably make payments:
1. Small businesses with tight budgets:
- A semi-monthly pay schedule provides stability with fewer payouts (24 vs. 26 annually). This makes it easier to predict cash outflows and plan for expenses.
2. Companies with steady revenue streams:
- For large businesses or institutions with consistent income, bi-weekly payments allow for more paychecks, spreading expenses evenly throughout the year.
3. Months with three pay periods:
- Remember, a bi-weekly schedule occasionally results in months with two paychecks plus an extra paycheck. While employees often welcome these months, employers must plan their budgets accordingly.
Tip: Review cash flow projections to assess if your business can sustain payroll on a bi-weekly basis or if a semi-monthly payroll schedule would better suit your needs.

Step 3: Streamline payroll processing
Processing payroll efficiently is essential for both bi-weekly and semi-monthly payroll schedules. Here are strategies to streamline operations:
1. Use automated systems:
Invest in payroll software to manage main pay schedules effectively. Automation reduces errors, ensures compliance, and saves time for HR teams. For instance, using tools like the wix affiliate app, setting specific dates for paid semi-monthly workers eliminates manual scheduling issues.
2. Account for holidays and weekends:
Whether you opt for semi-monthly vs bi-weekly, ensure payday falls on a business day. For semi-monthly schedules, adjust for holidays so employees don’t have to wait unnecessarily for their first paycheck of the month.
3. Track benefit deductions accurately:
Automation also helps with calculating and deducting benefits from paychecks, whether processing bi-weekly or semi-monthly payments. This step avoids discrepancies that could frustrate employees.
Tip: Regularly review and refine your payroll process to ensure it stays efficient and scalable as your business grows.
Step 4: Communicate with employees on semi-monthly pay schedule
Effective communication is crucial to successfully implementing any payroll schedule. Misunderstandings about pay dates or the frequency of two paychecks per month can lead to confusion and dissatisfaction. Here's how to avoid these pitfalls:
1. Educate employees on payment frequency:
Explain the differences between semi-monthly vs bi-weekly schedules. For example:
- Semi-monthly payments: Highlight the fixed nature of set dates and how this helps with long-term financial planning.
- Bi-weekly payments: Emphasize the benefit of more paychecks annually and how occasional months with three paychecks can provide extra income.
2. Outline the benefits of the chosen schedule:
Show employees how the schedule aligns with their preferences and financial habits. If you’ve chosen semi-monthly payments, stress the reliability of receiving pay on specific dates like the 15th and 30th. For bi-weekly payments, underline the consistent cash flow provided every two weeks.
3. Provide clear timelines:
Share a detailed calendar showing when each payday falls, including adjustments for holidays or weekends. This transparency builds trust and prevents confusion.
4. Offer support for questions:
Ensure employees have access to HR or payroll representatives to clarify questions about their first paycheck, deductions, or adjustments to pay schedules.
Tip: A proactive approach to communication minimizes misunderstandings and ensures employees feel valued and informed.

Why the choice matters
Selecting between semi-monthly vs bi-weekly pay impacts not only how employees receive their wages but also the efficiency of your business operations. By understanding the nuances of each schedule, you can improve employee satisfaction, streamline payroll frequency, and maintain financial stability. Whether you prioritize fixed pay dates or frequent payroll runs, the key is to align your choice with the needs of your workforce and business model.








